

Read the full paper “Long-Term Up-regulation of Inflammation and Suppression of Cell Proliferation in the Brain of Adult Rats Exposed to Traumatic Brain Injury Using the Controlled Cortical Impact Model” on PLOS ONE.

They go on to suggest a “multi-pronged treatment targeting inflammatory and cell proliferative pathways” may help alleviate the pathological effects of chronic TBI.
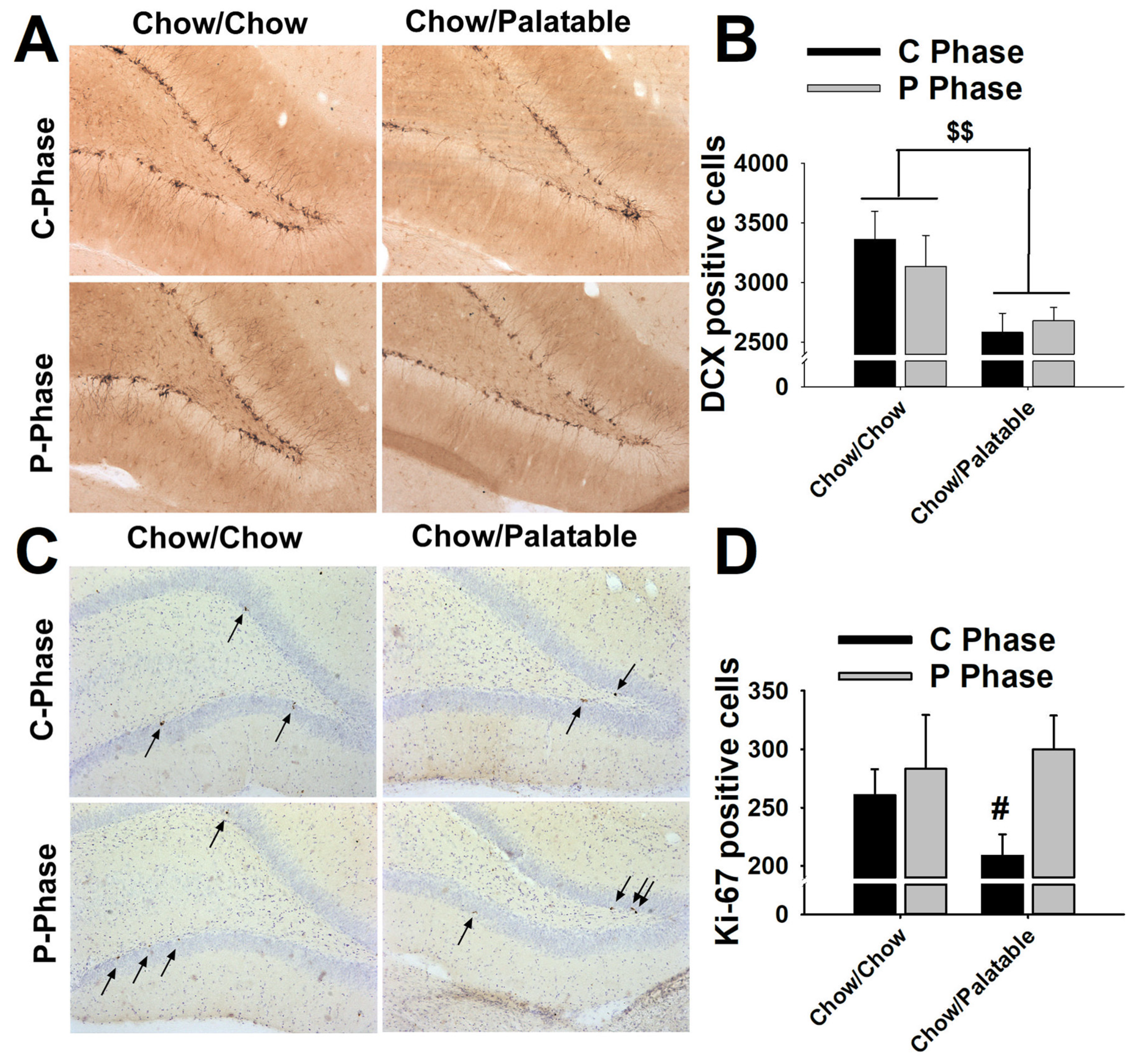
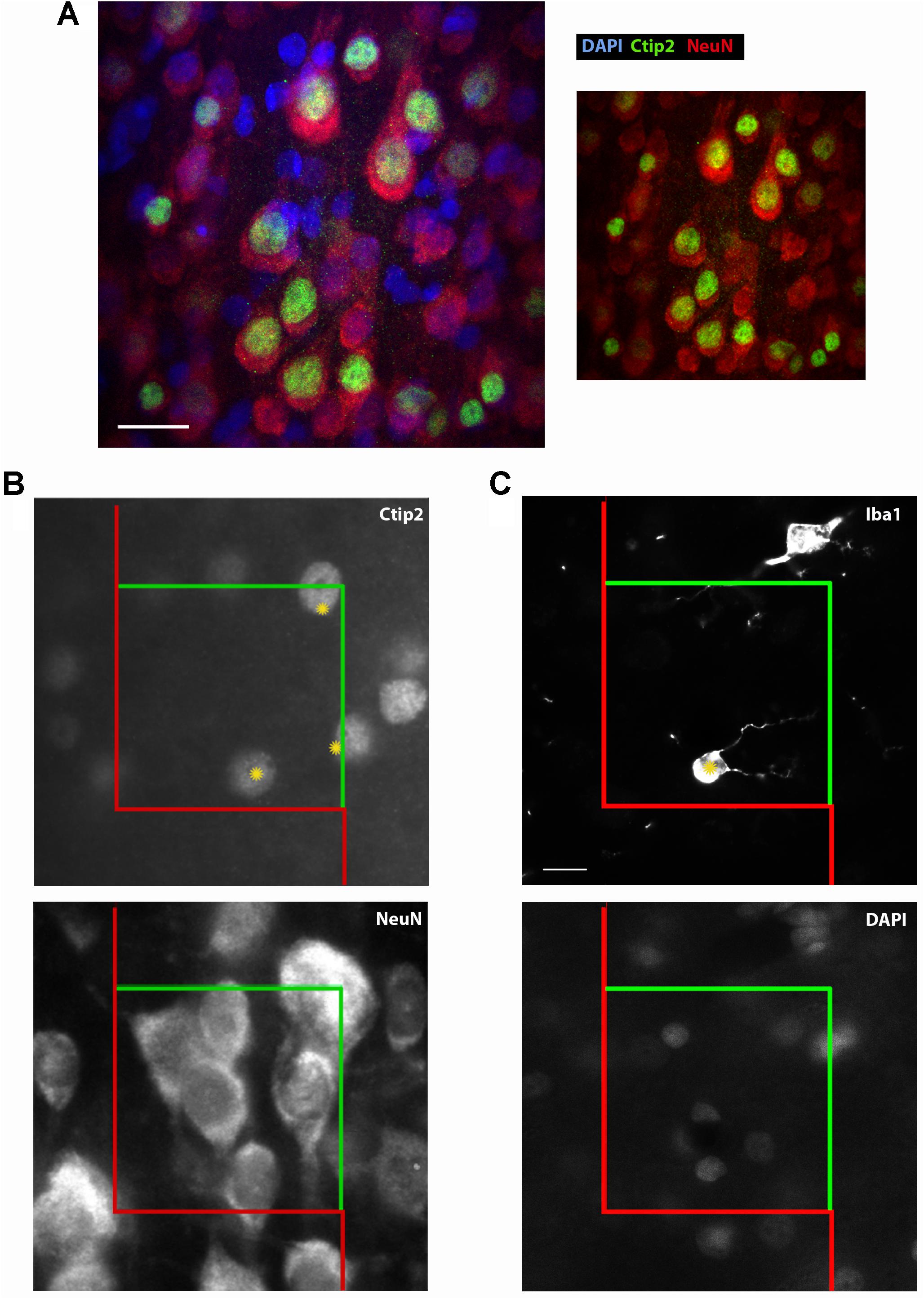
“Our overarching theme advances the concept that a massive neuroinflammation after TBI represents a second wave of cell death that impairs the proliferative capacity of cells, and impedes the regenerative capacity of neurogenesis in chronic TBI,” the authors say in their paper. They also report a decrease in hippocampal neurons, and low levels of cell proliferation in the neurogenic niches. They used Stereo Investigator with the Cavalieri estimator probe and the optical fractionator probe to estimate the quantity and volume of stained cells in the cortex, striatum, thalamus, fornix, cerebral peduncle, and corpus callosum, as well as the subgranular zone and the subventricular zone in both hemispheres of the brain.Įight weeks after the TBI occurred, the researchers found an increased level of active microglia cells at the direct site of the TBI as well as surrounding regions. The scientists used unbiased stereology to analyze activated microglia cells, cell proliferation, and differentiation into immature neurons in several regions of the brains of rats which had experienced TBI eight weeks prior. “While TBI is generally considered an acute injury, a chronic secondary cell death perturbation (i.e., neuroinflammation) and a diminished endogenous repair mechanism (i.e., cell proliferation) accompany the disease pathology over long-term,” the authors say in their paper published this month in PLOS ONE. When properly applied, fluorescent probes are ideally suited to the three-dimensional sampling requirements of the optical fractionator procedure.Researchers at the University of South Florida say patients suffering from chronic Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) experience a “cascade of events” marked by long-term neuroinflammation, cell loss, and impaired cell proliferation that may manifest over time. The chapter concludes with a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of using fluorescent probes for quantitative stereology. It also describes the limitations of fluorescent probes and cautions about their analysis. It demonstrates the advantages of fluorescent probes for optical sectioning and the preservation of section thickness that results from the preparative methodology making staining with fluorescent probes particularly useful for the implementation of the optical fractionator procedure. The theoretical and practical considerations for using fluorescent probes in quantitative analysis are presented along with a worked example using the optical fractionator procedure. This chapter describes the use of fluorescent probes in cell-counting procedures. Chapter 15 Unbiased morphometrical techniques for the quantitative assessment of cells in primary dissociation cultures.Chapter 13 Virtual test systems for estimation of orientation-dependent parameters in thick, arbitrarily orientated sections exemplified by length quantification of regenerating axons in spinal cord lesions using isotropic, virtual planes.Chapter 12 Length estimation of nerve fibers in human white matter using isotropic, uniformly random sections.Chapter 10 Estimation of number and volume of immunohistochemically stained neurons in complex brain regions.Chapter 9 The nucleator and the planar and optical rotators applied in rat dorsal root ganglia.Chapter 7 The number of microvessels estimated by an unbiased stereological method applied in a brain region.Chapter 6 Number in electron microscopy: estimation of total number of synapses in the main regions of human neocortex.Chapter 5 Counting in situ hybridized neurons.The optical dissector provides unbiased estimates of cell numbers independent of assumptions on the size and shape of the cells. Chapter 4 The use of fluorescent probes in cell-counting procedures The optical fractionator combines two stereological components: a three-dimensional probe for counting cell nuclei, the optical dissector, and a sampling scheme, the fractionator.An in situ hybridization study using the optical fractionator method. UNBIASED STEREOLOGY: DESIGN-BASED VERSUS MODEL-BASED METHODS. The distance between the sections and the area of the two sections define the volume of a disector probe. Alternatively, for cell number estimates, Fractionator sampling can be used (as described above), which is insensitive to shrinkage 9, 34. Chapter 2 A case study from neuroscience involving stereology and multivariate analysis A 3D probe can be constructed by using two sections, hence the name disector. Stereology avoids the bias of the reference trap through obtaining an unbiased estimate of the reference volume before any other parameters are measured.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
